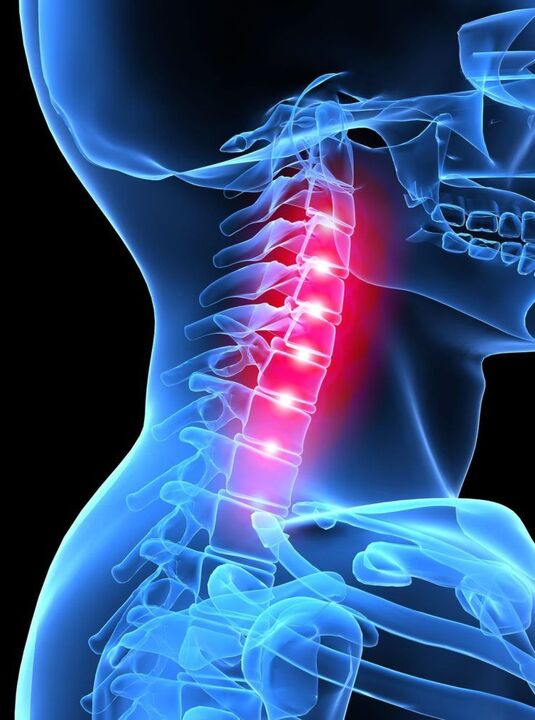
Cervical osteochondrosis is a spinal disorder characterized by disc degeneration, its height is significantly reduced, reactive growth of marginal osteophytes, and disc sclerosis.
The vertebrae in the cervical region are close enough to each other. The muscular structure in this area is relatively underdeveloped, so cervical osteochondrosis can cause disc displacement even under mild stress, which in turn compresses nerves and blood vessels.
The intervertebral disc cartilage tissue affected by osteochondrosis gradually transforms and degenerates into bone formation. As a result, the discs become stiffer and smaller, eventually losing the cushioning properties between the discs, putting pressure on the nerve endings and further pain.
The intervertebral discs in the neck area are fibrocartilaginous plates. In the middle of the disc is the nucleus, surrounded by an annulus fibrosus, a tendon-like tissue. Intervertebral discs do not have a vascular system, so nutrition occurs with the help of other tissues.
An important source of intervertebral discs is the spinal muscles, and it is their dystrophy that contributes to the symptoms of osteochondrosis. During weightlifting, jumping or other physical exertion, the shock absorbing function of the spine maintains the necessary distance between the vertebrae. This disease is a pathology. The following figure.
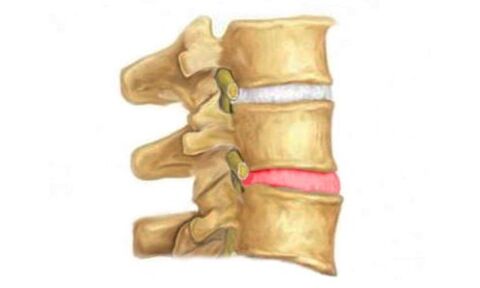
I would like to emphasize that because a protrusion (the main sign of osteochondrosis) is more likely to form in the lumbar spine, there is a complication - an intervertebral hernia.
A herniated disc is a prolapse (herniation) of an intervertebral disc without rupture of the annulus fibrosus.
Outflow of the nucleus pulposus, or rupture of the annulus fibrosus, is the final stage of a herniated disc—the final stage of osteochondrosis.
Development reasons
- Infect.
- revel.
- Metabolic disease.
- age changes.
- Genetic susceptibility.
- Lack of fluids and vitamins in the diet (malnutrition).
- Spinal cord injury.
- overweight.
- bad ecology.
- Postural disorders.
- Lazio Campsis.
- flatfoot.
- A sedentary physical lifestyle.
- Spinal segment instability.
- Being in an uncomfortable position (compressed disc) for a long time.
- Frequent shaking movements or changes in body position.
- Spine overload due to the use of uncomfortable shoes, such as high heels.
- Physical exercise.
- Uneven development of the musculoskeletal system.
- Pregnant.
- stressful situation.
- Excessive drinking.
- smokes.
- low temperature.
- Stay in a cold environment for a long time.
- Nervousness.
signs and symptoms
Cervical osteochondrosis has the following symptoms:
- dizziness, headacheIt should be emphasized that, in most cases, the signs of cervical osteochondrosis are accompanied by a headache. This condition is associated with pressure on blood vessels in the neck and head. Often, these symptoms and pain syndromes can cause severe discomfort that reduces performance. In addition, the headache is exacerbated with various movements of the body;
- DizzinessOccurs when the head is turned sharply to one side;
- chest and arm painDuring cervical osteochondrosis, signs very similar to those of angina pectoris are burning or tenderness of the heart. In most cases, hand pain is accompanied by tingling and numbness;
- low back pain- This is the most common symptom of cervical osteochondrosis. An unpleasant feeling like intense pain extending to the fingers of the hand;
- Tongue numbness. The presence of symptoms of this cervical osteochondrosis can result in restricted tongue movement. In this regard, many patients complain about the pitch of the vocal cords (they become very rough) and changes in speech.
diagnosis
Therefore, diagnosis and treatment are carried out by medical specialists - chiropractors, orthopedists, neurosurgeons in the presence of a visual examination of the patient, in conjunction with complaints of limited mobility or deformity. Examine patients in a sitting, lying, standing, resting, or exercising position. The extent of damage to the spinal area is determined according to a special protocol.
Determine the location, extent, and nature of pain by feeling the spine, increasing muscle tone along the spine. Bending, turning, flexing the body indicates the range of motion of the affected area.
In the future, MRI, computed tomography or radiography will be used to diagnose osteochondrosis. Checking the condition of the blood vessels in the cervical region requires an appointment for a duplex scan or an ultrasound tomography scan.
treat
Cervical osteochondrosis and its complications are treated with a conservative approach aimed at eliminating pain syndromes, spinal root dysfunction, and preventing the progression of dystrophic changes in the spinal structure. In the case of ineffective conservative treatment, according to certain indications, surgical (surgical) treatment is performed, and the amount of treatment depends on the clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis and the level of the lesion.
Treatment of osteochondrosis is directly dependent on the severity of the disease course, age-related changes, the treatment used, and the careful implementation of the attending physician's recommendations and prescriptions. Often, cervical pain increases at the start of treatment but soon stops with the use of medication, physical therapy procedures, and physical procedures and therapeutic massage.
The most effective outcome in the treatment of osteochondrosis is a comprehensive treatment of the disease of the entire musculoskeletal system.
practise
Exercises and gymnastics for cervical osteochondrosis can help reduce pain, strengthen cervical muscles, and make osteochondrosis less likely to recur.
- recommended fromA simple exercise - ten sharp turns of the cervical spineGymnastics are performed as follows: the head is turned in one direction while freezing at one point for a few seconds, then the process is repeated in the other direction. When practicing, keep your head down and look straight ahead.
- Exercise - Head Tilt. The head is tilted to the left to contact the shoulder joint with the ear, the shoulder must remain relaxed. We repeat on the right. The above exercise restores shock absorption. The following figure.
- Stretching exercises for neck muscles.We bend our necks and tilt our heads back and forth. As you move forward, press your chin against your chest and hold it in a similar position for a few seconds. As a result, we screwed the head back to its original position and tilted it back. Practice repeating ten times.
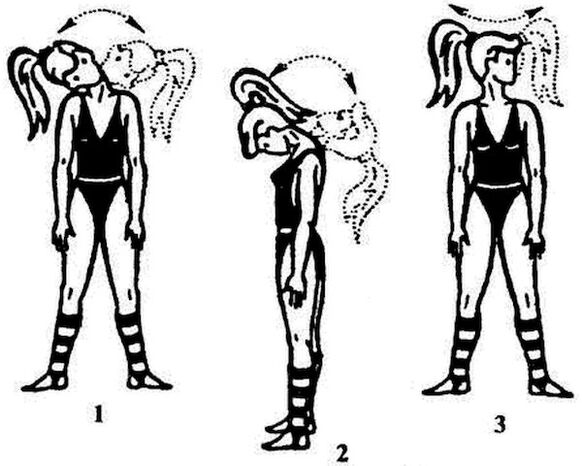
As you can see, neck exercises or gymnastics are very simple but very effective. The main thing is to exercise regularly..
massage
Osteochondrosis is not a word! Medication, massage, therapeutic exercise are possible at home.
A cervical spine massage with osteochondrosis is performed in the presence of someone close to you. Massage oils are used to relieve discomfort.
To perform this procedure, prepare the neck so that the patient is placed on a wide surface and the folded towel is placed under the shoulder blades.These movements will help stretch the neck muscles and lengthen the spine. For a while, the patient's muscles relax. As a result, the patient sits in a chair with his back straight..
After a certain time, lubricate the neck with massage oil. The oil is considered a remedy for headache relief. This oil, which usually contains capsaicin, produces heat when applied, providing a comfortable environment while the massage is being performed.
So, the massage begins as follows, the trapezius is groped, descending from the upper neck to the shoulders. Knead it hard to feel the pressure, but gently, without pain. Use the right hand to massage the muscles on the left side. Count each muscle for five minutes, then let it rest and repeat again.
The massage is done by wrapping the massage area with a hot towel, after which bed rest is required.. Proper massage movements can cause drowsiness.