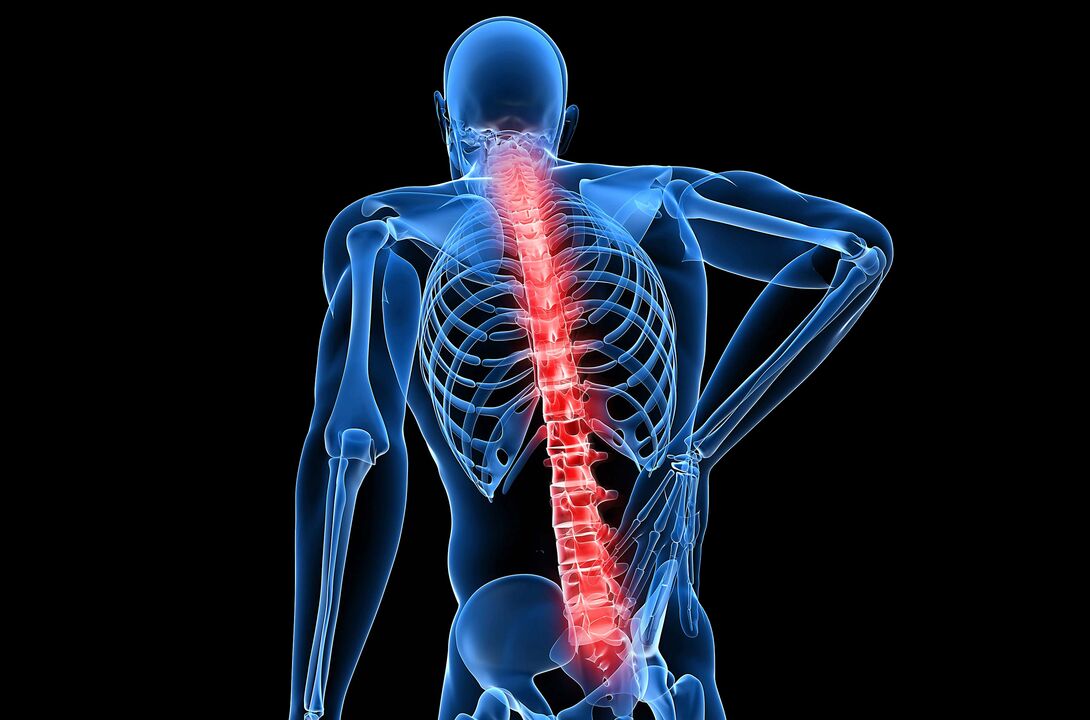
What is lumbar osteochondrosis?
Possible complications of the disease
- Sciatica;
- Spinal deformity;
- loss of sensation in the limbs;
- spinal instability;
- Pathology of internal organs;
- Radiculitis;
- Complete loss of motor activity.
Main symptoms and signs of lumbar osteochondrosis
- Lower back pain. In the early stages of the disease, symptoms may appear only after lifting weights. As the pathology progresses, the pain syndrome becomes unbearable.
- Reduced physical activity. This symptom is caused by compression of nerve fibers. When bending or turning, discomfort may occur and radiate to the leg.
- Loss of sensation in the lower limbs. As lumbar osteochondrosis progresses, the nerve roots are permanently damaged and numbness occurs. The symptoms increase and decrease periodically. In this condition, patients experience burning, numbness, and tingling in the waist and below.
- Local skin temperature decreases. It becomes pale, dry, and flabby.
- Excessive sweating.
- Spinal Syndrome. This symptom appears in advanced cases. People often experience sexual dysfunction and urinary problems.
Causes of lumbar osteochondrosis
- Bad posture.
- Lack of physical activity. Lack of physical activity can lead to muscle weakness.
- Calcium metabolism disorder.
- Long-term deficiency of trace elements and macroelements. This may be due to an eating disorder.
- Genetic susceptibility.
- Low temperature.
- stress factors.
- Strength or extreme sports.
- Damage to the musculoskeletal system.
- excess weight.
What are the stages of the disease?
- First, at this stage, waist pain is bearable and will worsen after exercise. This symptom indicates a destructive process on the disk. Patients may experience burning and stinging sensations. Sometimes these symptoms radiate to the buttocks.
- Secondly, at this stage, the distance between the vertebrae decreases and the annulus fibrosus is destroyed. The patient will experience severe pain. It radiates to the buttocks, buttocks, and legs during exercise. The affected area may feel cold or burning. During the attack, the patient is forced to lean in the opposite direction.
- Third, the annulus fibrosus is completely destroyed at this stage. The spinal tissue is severely deformed. This can cause an intervertebral hernia to develop. As this degree of lumbar osteochondrosis progresses, persistent, high-intensity pain occurs.
- The fourth is accompanied by abnormal intervertebral disc growth and bone destruction. At this stage, the cartilage tissue is severely atrophied. This can lead to disruption of a person's motor activities and even lead to disability.
When should you see a doctor?
- Stop inflammation;
- Strengthen leg musculature;
- Eliminate pain syndrome;
- Improves metabolic processes and blood circulation;
- normalizes the function of pelvic organs;
- Restore sensitivity.
- NSAIDs. They help deal with swelling and inflammation. Therefore, the compression of blood vessels and fibers can be eliminated and pain can be relieved. The most effective drugs include diclofenac and nimesil.
- Painkillers. They are prescribed during pathological exacerbations and are accompanied by severe pain. These medications have many side effects. Therefore, they must be prescribed by a doctor. Most commonly, Baralgin or Pentalgin is prescribed.
- Muscle relaxants. These treatments can help manage muscle spasms. This allows you to eliminate discomfort. This category includes Mydocalm, Sirdalud.
- Glucocorticoids. These are hormonal preparations that help deal with inflammation and improve the function of the nervous system. The drug Ambene is very effective.
- physiotherapy. Performing special exercises can help strengthen your muscles. This helps create correct posture, increases ligament flexibility, and prevents complications of osteochondrosis. Gymnastics improve blood circulation, normalize metabolic processes, increase the distance between vertebrae and reduce the load on the vertebrae.
- Manual therapy. It involves using personal manual techniques to help control pain and improve posture. This treatment restores motor activity, normalizes blood flow, strengthens the immune system and activates metabolic processes.
- massage. This process can have a relaxing or tonic effect on the body. With its help, the load on the muscles is relieved, blood flow is stimulated and lymphatic drainage is activated. Massage can also relieve pain and have a restorative effect.
- physiotherapy. For lumbar osteochondrosis, ultrasound, low-frequency current, and magnetic fields may be used. This helps relieve pain, relieve inflammation, and normalize blood circulation. Physiotherapy products stimulate the healing process and increase the effectiveness of medications.
Prevention of lumbar osteochondrosis
- Avoid lumbar hypothermia;
- control posture;
- exercise;
- Change body position while performing monotonous tasks;
- Refusal to lift heavy objects;
- Healthy Food.
How is treatment performed in modern clinics?
- Spinal pain - MRI or CT (magnetic resonance or computed tomography) of the problem area;
- Joint pain – X-ray;
- Presence of concomitant diseases - medical history or outpatient card extract;
- Comfortable (athletic) clothes and shoes
Take classes with a coach
- How long have you had this problem (stage of disease)
- How your body prepares for physical activity (whether you do gymnastics or any sport)
- Relieve aggravation? One or two cycles is enough
- Restoration of function, walking without stopping (climbing stairs), stooping, performing certain tasks without effort, remaining still for long periods of time while traveling, general improvement, may require three or more treatment cycles