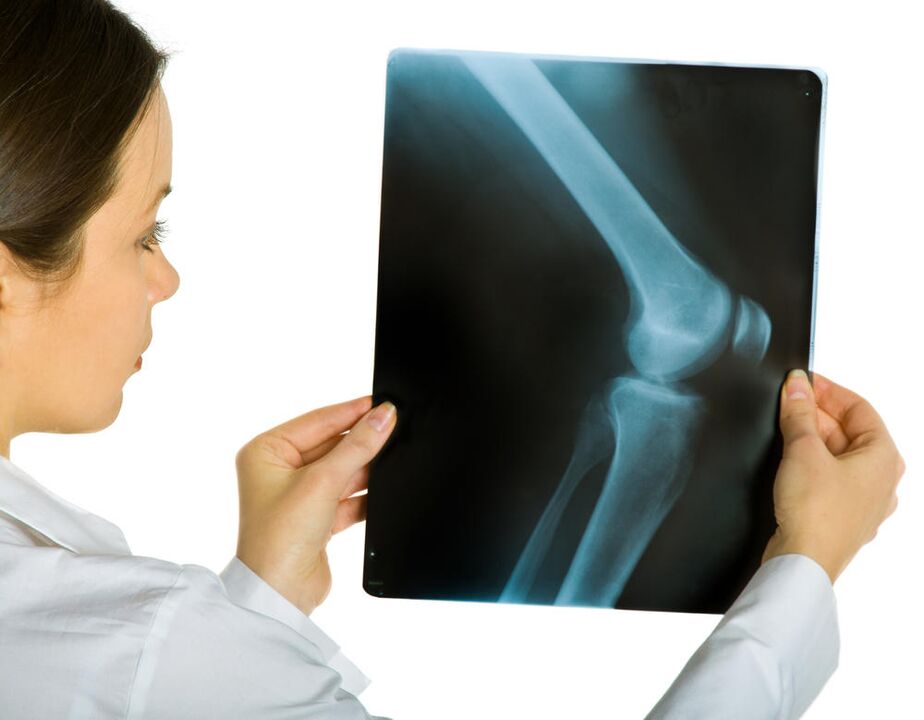
Up to 20 percent of people over the age of 25 are at risk of developing osteoarthritis of the knee joint. The knee joint functions in an axial compression mode, so its articular surfaces are under constant load and undergo degenerative changes in the hyaline cartilage.
%20and%20a%20knee%20affected%20by%20arthrosis%20(left).jpg)
Prevalence
The pathology of degenerative dystrophic articular cartilage with the participation of bone tissue, joint pockets, ligaments and muscles is called osteoarthropathy. There are synonyms in the term:
- Osteoarthritis;
- Osteoarthritis;
- degenerative arthritis;
- joint;
- hypertrophic arthritis;
Injuries to the knee follow closely behind the hip in terms of frequency, thus forming a stable phrase: "knee arthrosis". The dependence of disease frequency on age was studied:
| 26 - 44 years old | 5% of adults |
| 45 - 59 years old | 16. 70% |
| 60 - 69 years old | 12. 10% |
| over 70 years old | eleven% |
In all age groups, representation of the fair gender is numerically dominant. Among them, the incidence of knee joint disease is 1. 2-1. 4 times that of men.
In the area of persistent disability, osteoarthropathy of the knee accounts for almost 30% of all joint pathology-related disabilities.
Classification of Knee Arthropathy
For developmental reasons, the disease is divided into two main categories: primary and secondary. There are no visible prerequisites for major occurrences. Secondary precedes (or accompanies) provocative factors:
- Biomechanical disorders: injury, overload, dysplasia (dysplasia), skeletal pathology (scoliosis, flat feet), obesity;
- Inflammatory processes: aseptic or infectious arthritis, frequently hemarthrosis in hemophilia;
- Metabolic diseases: gout, hemochromatosis, Paget's disease;
- Endocrine gland diseases: acromegaly, diabetes, parathyroid disorders;
- Violation of adequate blood supply: varicose veins and post-thrombophlebitis syndrome, endarteritis obliterans, atherosclerosis of vessels of the lower extremities;
In medical practice, classification according to the severity of lesions is more useful. Evaluation is based on X-ray studies. The most popular clinical and radiological classifications.
i stage
The picture shows that the joint space has narrowed slightly (compared to a healthy joint) and the bone tissue around the cartilage has begun to harden. Clinically - Pain occurs during or immediately after walking, prolonged standing. It is more noticeable when going up stairs. Pass on break. Grade 1 knee arthrosis does not seriously affect the function of the joint.
Phase II
The joint space is 2-3 times narrower than normal. Sclerosis is more pronounced and osteophytes (sharp growths of bone tissue along the joint spaces and edges of the condyles) are found. The pain was moderate, with signs of muscle atrophy and limping. Deformation of the knee on the frontal axis is visible. Grade 2 knee arthropathy results in markedly limited range of motion.
Phase III
The cartilaginous elements harden and the articular surfaces deform. There are areas of subchondral necrosis and localized osteoporosis. A cyst in adjacent bone tissue. The joint space is severely narrowed, sometimes ill-defined. Sizable osteophytes. The thigh and calf muscles were atrophied, the joints were unstable, and there was obvious deformity. Movement of the knee is sometimes impossible, forming a contracture. When moving - severe pain, limp.
This classification is convenient because it allows assessment of clinical manifestations associated with organic changes. It gives you the opportunity to choose a more effective treatment based on a comprehensive assessment of the state of your joints.
development mechanism
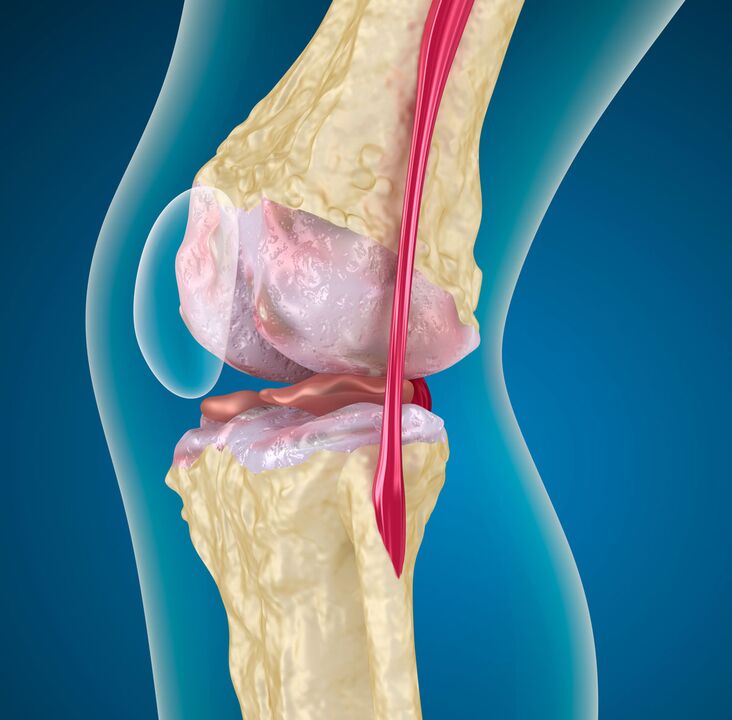
The pathogenesis of any joint disease goes through three stages:
- Damage to cartilage microstructure. Under the influence of any destructive factors, the polymer compound loses its strength and becomes enriched with water molecules. The ability of low molecular weight collagen to assemble into large molecules is impaired. This results in a decrease in the strength and durability of the hyaline cartilage. Chondroprotectants counteract this phenomenon.
- The weakening of cartilage components (glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans) continues if the provocative factor is not eliminated. This results in the activation of the recovery process. They don't have a particularly large power reserve, so one stage quickly moves on to the next.
- Disruption of compensatory mechanisms leads to the gradual destruction of articular cartilage, the death of its cells - chondrocytes. Cartilage cracks extend into the underlying bone. The degree of detachment of cartilage components increases, and fibrosis occurs, resulting in thinning of the hyaline membrane.
On the skeletal side, as the knee joint deforms, it thickens (hardens), develops cysts and areas of uneven bone density. As a result, deformation of the articular surface, instability of the joint develops.
diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on a set of data obtained through investigation (history), medical examination, and instrumental research methods. The latter include radiography (CT, MRI), radioisotopes (scintigraphy), arthroscopy.
objective test
It includes clarification of the patient's life history, conditions prior to the development of chondrosis of the knee, collection of complaints, and examination. In the process, the presence of predisposing factors and the extent to which they influence disease development are elucidated.
At this stage, it is important to find out the condition of the second knee. If you miss bilateral knee joint disease and focus only on the knee that worries you more, you could be making a serious diagnostic error.
For this purpose, functional tests should be performed on both limbs simultaneously. Note pain with active and passive movements, sensitivity to palpation, and crepitus (crunching) during extension and flexion. A chronic inflammatory process leads to the appearance of a Becker's cyst - a joint bag protruding into the popliteal fossa, which can also be detected by palpation.
Instrumental method
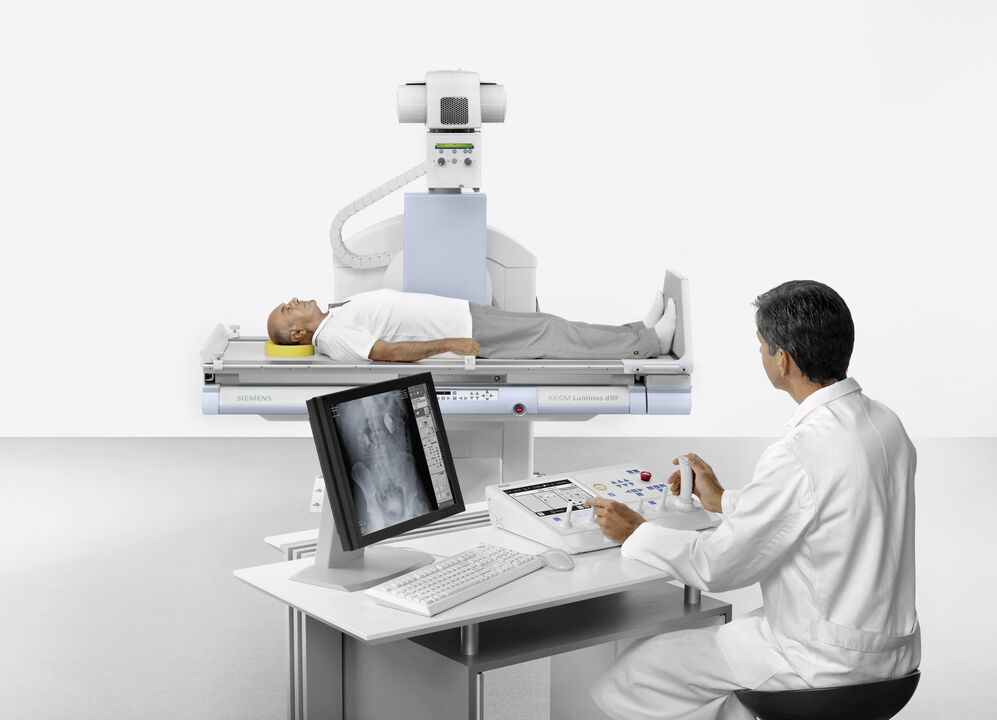
The first is radiography. Pictures of the knee in two projections allow an initial assessment of the condition of the joint and determination of the stage of the disease. The disadvantage of this approach is that the radiographic signs are later than the symptoms and morphological changes that accompany knee arthropathy.
In this case, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) can help. The initial stages of degenerative changes in cartilage and bone structures can be determined, and the state of intra-articular ligaments and menisci can be assessed. Scintigraphy in chondrosis of the knee provides data on functional status.
Arthroscopy allows direct examination of the joint cavity.
For the harmonization of diagnostic data, the American College of Rheumatology proposes the following criteria:
- Are over 50 years old.
- Joint stiffness in the morning for at least half an hour.
- Cracking, determined by movement (active and passive).
If these symptoms are accompanied by osteophytes and pain found on radiographs, chondrosis of the knee is very likely.
The initial stages of the disease may not be evident, so a differential diagnosis with other arthropathies is necessary where osteoarthritis-causing drugs (chondroprotectants) will not be effective.
All possible steps should be taken not to confuse knee arthrosis with:
Rheumatoid Arthritis |
Early onset, morning stiffness for more than 30 minutes, increased pain when resting, lessened pain when exercising, rheumatoid nodules on the skin, accompanying lesions on internal organs, symptoms of poisoning (fever, sweating), C-reactive protein in blood tests. |
Crystal Arthritis |
Severe pain, at night or in the morning; edema, redness, warmth of the skin over the affected joint; crystallization on microscopic examination of the synovial fluid, increased uric acid in the blood (with gout). |
Spondyloarthropathy |
Arthritis of other non-joint joints (intercostal, lumbar joints); inflammatory processes of tendons; damage to the cornea, skin, mucous membranes. |
In the tenth revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10), all of these diseases are assigned the index "M", but with different numerical codes.
These are fundamentally different pathological processes that require professional diagnostic methods and qualified treatment.
treatment measures
If there is a disease, there must be a way to cure knee joint disease. they exist. Help can be provided in a number of ways.
The first is the achievements of traditional medicine based on in-depth research on the etiology and mechanism of diseases. Here medical and surgical methods are used. Effective treatment requires continuous and complex use of medications, physical therapy and rehabilitation.
The second method is to treat with folk remedies. To put it mildly, the effectiveness of these methods is questionable. But they are used because it is possible to reduce the manifestations of the disease at home. Folk remedies can only be used as a supplement to drug treatment or as part of comprehensive therapy, and must be approved by the attending physician!
drug help
This type of treatment involves the use of various medications. For efficacy, drugs from different groups are used:
- NSAIDs, analgesics, opiates;
- Slow-acting symptomatic drugs (chondroprotectants);
- glucocorticoids;
NSAIDs, rapid pain relievers, opioids
This group of medicines is designed to eliminate pain. Pain syndrome almost ruins the life of arthropathic patients and its removal can significantly improve human quality of life. NSAIDs, anilines, non-narcotic and narcotic pain relievers can do this.
A common disadvantage is side effects. These drugs can negatively affect the protective mechanisms of the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract. An alternative method that may reduce deleterious manifestations is injections. Intramuscular administration has little damage to the stomach and has a quick effect.
Due to side effects, drugs of this group are prescribed during exacerbations, which require careful selection of doses.
The main advantage of NSAIDs is the variety of forms of topical treatment (ointment, gel). Allows you to manage the manifestations of the disease at home.
Central analgesics were prescribed for a short period of time, and the other two groups were ineffective. The most prevalent opioids were prescribed during exacerbations, more commonly in bilateral knee arthrosis. These drugs are addictive. You can't take them yourself!
Slow-acting drugs
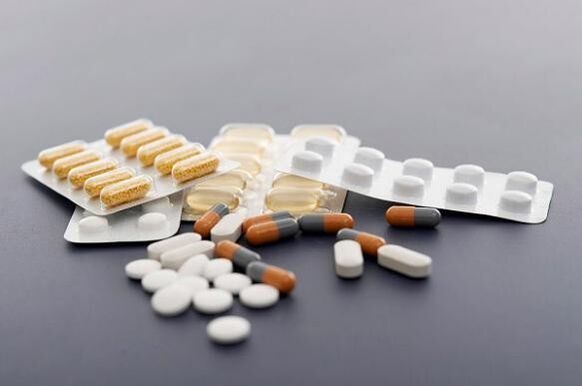
The action of these substances is twofold: they reduce pain (like NSAIDs) and help restore hyaline cartilage. They are often called chondroprotectants.
Effects last for several weeks (2-8) and 2-3 months after withdrawal.
In addition to chondroitin sulfate and glycosaminoglycans, this group also includes preparations based on hyaluronic acid, compounds derived from avocado and soybean.
The most researched and popular chondroprotectants (chondroitin sulfate and glycosaminoglycans) are readily available components of articular cartilage. It is well absorbed into the blood and forms a high concentration in the joint cavity. For faster results, it can be injected directly into the joint.
Chondroitin sulphate has been shown to have a stabilizing effect on the joint space in grade 2 chondrosis of the knee at a dose of 800 mg per day for a two-year course.
The avocado/soy compound is anti-inflammatory. Thanks to the inhibition of collagenase (a decomposing enzyme), they significantly slow down the destruction of cartilage and increase the synthesis of "own" collagen. They are also well tolerated.
Hyaluronic acid derivatives are used in the form of intra-articular injections. These funds, like cartilage protectors, improve the functional status of the knee joint.
Various slow-acting drugs have different mechanisms of action, so combined use is recommended. The high level of safety allows you to take chondroprotectants for a long time without significant harm to your body.
Glucocorticoids
The main function is anti-inflammatory. These funds prescribe NSAIDs when they are not effective. The tablet form can also damage the stomach lining. There are forms for intra-articular injections.
They have many side effects, so you should not abuse steroids for osteoarthritis of the knee.
team name |
advantage |
flaw |
|---|---|---|
NSAIDs, pain relievers, opioids |
Quick effect, many forms of external application. |
Side effects, unstable effects, dangerous for age-related patients, prone to addiction. |
Chondroprotectant |
They are pathogenic, long-lasting, non-toxic and available in topical and intra-articular forms. |
The effects develop slowly. |
hormone |
Rapid action in the absence of NSAIDs; intra-articular form. |
The side effects are large, the effect is unstable, and it is impossible to take it for a long time. |
ethnic science

At home, you can reduce the manifestations of the disease with folk remedies. There are many recipes, but a few but:
- Clinical studies have not yet been conducted;
- Impossible to dose the drug accurately;
- Indications are not clearly defined;
- Failure to take into account individual tolerance to folk remedies;
The advantage is that it has a wide range of treatment and many options for external use. Homemade compresses and tinctures, ointments are popular.
The effectiveness of home remedies is confirmed by the fact that biologically active substances (chewing gum, bile, infusions of medicinal plants) are used in the preparation.
Additionally, effective folk remedy treatment begins with adhering to a diet and losing weight. Only this method, aimed at reducing the load on the joints, can reverse the grade 1 osteoarthritis of the knee joint (conditions are young age and sufficient compensatory ability). A healthy diet itself stimulates the body's regenerative abilities. Diet includes: light hunger pangs, vegetables, freshly squeezed juices. It is recommended to add low-fat jelly, jelly to the diet.
There are various external means. They are mainly irritating and warming. The most studied ingredients are bile, dimethyl sulfoxide, and bischofite. Bile should be used for medical purposes, not extracted from animal carcasses alone. Dimethyl sulfoxide is an analogue of the chemical warfare agent mustard gas. Bischofite is a derivative of petroleum. This is the difference of origin.
All three drugs have anti-inflammatory properties, however, they should only be used at home after consulting a doctor. These substances also have contraindications and application characteristics.
We must not forget the placebo effect in folk remedy treatments.
The last thing to convey is that people have a kind of health. You should not rely solely on the apparent simplicity and cheapness of folk remedies. If you've decided to try them, pay more attention to sore joints. The progression of the disease in the context of treatment with folk remedies is a reason to reconsider the approach to treatment.
If you are diagnosed with knee osteoarthritis of grade 2 or above, it is best not to use Chinese medicine indiscriminately. Or postpone until remission. Unsatisfactory treatment is an indication for complex surgical intervention.